Strategies and Tips:
Electrical substations are critical components of the power distribution network, playing a vital role in transforming voltage levels and ensuring the of electricity. Understanding how to prevent these faults is essential for maintaining the integrity of the electrical grid. This article explores and tips to effectively minimize the risk of electrical substation faults.
Understanding Electrical Substation Faults:
Before delving into prevention strategies, it is crucial to comprehend what electrical substation faults are and their potential impacts. Faults can occur due to various reasons, including equipment failure, environmental factors, and human error. The complexity of electrical systems means that even minor issues can escalate quickly, leading to in service and safety concerns.
Electrical faults can be broadly categorized into two types: short circuits and open circuits. A short circuit occurs when there is an unintended path for current flow, often leading to excessive current that can damage equipment and create safety hazards. On the other hand, an open circuit happens when there is a break in the electrical path, causing a loss of power supply. Understanding these basic types is essential for diagnosing issues and implementing effective solutions.
Additionally, faults can be classified based on their nature, such as single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase faults.
Consequences of Faults:
The consequences of electrical faults in substations can be severe. They can lead to power outages, equipment damage, and increased operational costs. In some cases, faults may even pose safety risks to personnel working in or near the substation. Understanding these consequences underscores the importance of proactive measures to prevent faults. For example, a single fault incident can trigger cascading failures throughout the grid, affecting not only the immediate area but also remote locations reliant on the same power source.
Essential Strategies for Preventing Faults:
Preventing electrical substation faults requires a multifaceted approach that includes regular maintenance, advanced monitoring technologies, and employee training. Here are some essential strategies to consider:
1. Regular Maintenance and Inspections:
One of the most effective ways to prevent faults is through routine maintenance and inspections. Regular checks of equipment, such as transformers, circuit breakers, and protective relays, can help identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems.
Maintenance schedules should include cleaning, testing, and replacing components that show signs of wear or degradation. Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities can also aid in tracking the performance of equipment over time and identifying trends that may indicate a need for further intervention.
2. Implementing Advanced Monitoring Systems:
Modern technology offers various solutions for monitoring the health of electrical substations. Advanced monitoring systems can provide real-time data on equipment performance, allowing operators to detect anomalies that may indicate an impending fault.
These systems can include sensors for temperature, vibration, and electrical parameters, enabling predictive maintenance strategies. By analyzing data trends, operators can make informed decisions about when to perform maintenance or replace equipment, significantly reducing the risk of faults.
3. Utilizing Protective Devices:
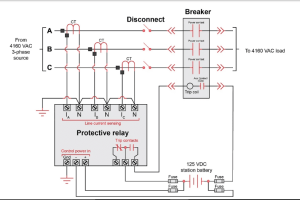
Protective devices such as circuit breakers, fuses, and relays are essential in safeguarding electrical substations against faults. These devices are designed to detect abnormal conditions and isolate affected sections of the network, preventing widespread outages and equipment damage.
Regular testing and calibration of protective devices are crucial to ensure their proper functioning. Operators should also familiarize themselves with the settings and operation of these devices to respond effectively in the event of a fault.
Environmental Considerations:
The environment surrounding an electrical substation can significantly impact its reliability. Various external factors can contribute to faults, including weather conditions, wildlife interference, and vegetation growth. Addressing these environmental considerations is vital for fault prevention.
1. Weather Resistant and Infrastructure
Substations should be designed and constructed with weather-resistant materials to withstand extreme conditions such as heavy rain, snow, and high winds. This includes using corrosion-resistant coatings on equipment and ensuring that structures can support the weight of accumulated snow or ice.
Additionally, proper drainage systems should be in place to prevent flooding, which can damage electrical equipment and create hazardous conditions. Regular inspections of the infrastructure can help identify vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
2. Wildlife Management:
Wildlife, particularly birds and rodents, can pose significant risks to electrical substations. Birds may perch on equipment, leading to short circuits, while rodents can chew through insulation and wiring. Implementing wildlife management strategies, such as installing bird deterrents and rodent-proofing equipment, can help mitigate these risks.
Human Factors in Fault Prevention:
Human error is a significant contributor to electrical faults in substations. Ensuring that personnel are well-trained and aware of best practices can help minimize the risk of mistakes that lead to faults.
1. Comprehensive Training Programs:
Developing comprehensive training programs for all personnel involved in the operation and maintenance of substations is crucial. Training should cover equipment operation, safety protocols, and emergency response procedures. Regular refresher courses can help keep knowledge current and reinforce the importance of following established procedures.
Additionally, hands-on training and simulations can provide valuable experience in dealing with potential fault scenarios, preparing personnel to respond effectively in real-life situations.
2. Promoting a Safety Culture:
Fostering a culture of safety within the organization is essential for preventing faults. Encouraging open communication about safety concerns and near-miss incidents can help identify potential issues before they lead to faults.
Recognizing and rewarding safe practices can also motivate personnel to prioritize safety in their daily operations. A strong safety culture not only reduces the risk of faults but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
Emergency Preparedness and Response:
Despite the best prevention efforts, faults can still occur. Having a robust emergency preparedness and response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of faults when they do happen.
1. Developing an Emergency Response Plan:
An effective emergency response plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a fault, including communication protocols, evacuation procedures, and coordination with emergency services. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in personnel, equipment, or procedures.
Conducting regular drills and simulations can help ensure that all personnel are familiar with the emergency response plan and can act quickly and effectively in a real emergency.
2. Establishing Communication Protocols:
Clear communication is critical during an emergency. Establishing protocols for reporting faults and communicating with relevant stakeholders, including management, emergency services, and affected customers, can help ensure a coordinated response.
Utilizing modern communication tools, such as mobile apps and instant messaging platforms, can facilitate rapid information sharing and improve response times during emergencies.
Case Studies and Lessons Learned:
Examining real-world case studies of electrical substation faults can provide valuable insights into effective prevention strategies. Analyzing past incidents can help identify common causes and highlight successful mitigation efforts.
1. Learning from Past Incidents:
Many electrical utilities have experienced faults due to equipment failure, human error, or environmental factors. By studying these incidents, organizations can develop a deeper understanding of the vulnerabilities within their systems and implement targeted strategies to address them.
For example, a utility that experienced repeated faults due to aging transformers may invest in a comprehensive replacement program, ensuring that all equipment meets current standards and is less prone to failure.
2. Sharing Best Practices:
Collaboration among utilities and industry organizations can facilitate the sharing of best practices for fault prevention. Participating in industry conferences, workshops, and forums can provide opportunities to learn from others’ experiences and adopt successful strategies.
Establishing partnerships with research institutions can also lead to innovative solutions and technologies that enhance fault prevention efforts.
Conclusion:
Preventing electrical substation faults is a multifaceted challenge that requires a proactive approach. By implementing regular maintenance, utilizing advanced monitoring systems, addressing environmental factors, and fostering a culture of safety, utilities can significantly reduce the risk of faults and enhance the reliability of their power distribution networks.
Explore In-Depth Guidance on Substation Fault Prevention:
Ready to dive deeper into the intricacies of electrical substation faults? Visit for a comprehensive guide that covers everything from the root causes and troubleshooting methods to advanced prevention strategies. Our platform is an essential resource for engineers looking to enhance the reliability and efficiency of electrical substations. Don’t miss out on expert advice and solutions.


3 Comments
substationfaults.com
substationfaults.com
substationfaults.com
substationfaults.com